Rotator Cuff Tear
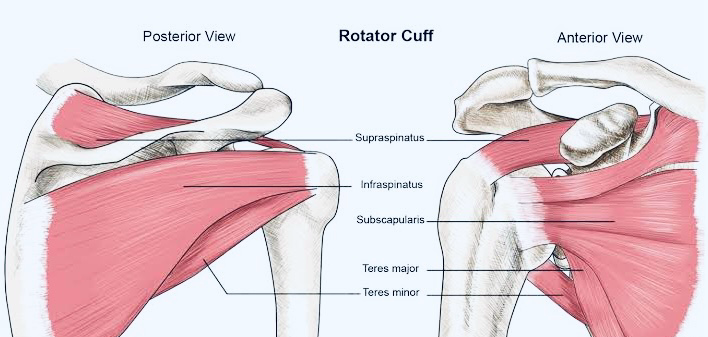
- Supraspinatus – Helps in lifting the arm (abduction).
- Infraspinatus – Responsible for external rotation at 0° abduction.
- Teres Minor – Assists in external rotation at 90° abduction.
- Subscapularis – Aids in internal rotation and balances arm movement.
What is a Rotator Cuff Tear?
A rotator cuff tear occurs when one or more of these tendons are damaged. It can be a partial tear or a complete tear. In many cases, rotator cuff tears are associated with AC joint problems
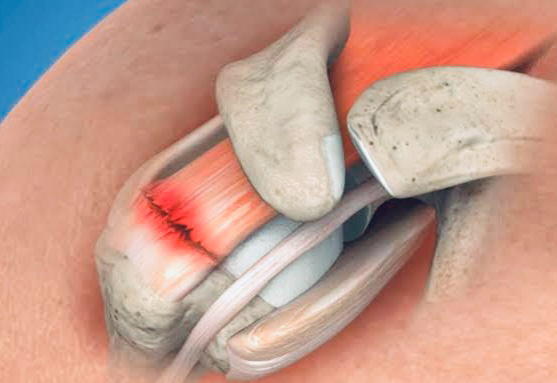
- Causes of Rotator Cuff Tears
- Chronic Degenerative Tears
- More common in older adults due to wear and tear over time.
- Usually affects the supraspinatus, followed by infraspinatus and teres minor.
- Can extend to the subscapularis in massive tears.
- Acute Avulsion Injuries
- Seen in younger individuals due to trauma or falls.
- Commonly affects the subscapularis.
- Can occur after a shoulder dislocation.
- Full-thickness tears in young athletes require surgical repair.
Functions of the Rotator Cuff
The rotator cuff muscles provide dynamic stability to the shoulder joint by maintaining a balance of forces across different planes:
- Coronal Plane Stability – Balances the deltoid muscle’s superior pull with infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis.
- Transverse Plane Stability – Maintains anterior-posterior balance between subscapularis and infraspinatus/teres minor.
The goal of treatment is to restore this balance and ensure proper movement of the shoulder.
Rotator Cuff Tear Size Classification
- Small Tear – 0-1 cm
- Medium Tear – 1-3 cm
- Large Tear – 3-5 cm
- Massive Tear – More than 5 cm, involving multiple tendons
Symptoms of a Rotator Cuff Tear
- Gradual onset of pain, worse with overhead activities.
- Night pain, which is often an indicator of a poor response to non-surgical treatment.
- Difficulty lifting the arm (painful or weak shoulder abduction).
- Problems with daily activities like combing hair or reaching behind the neck.
Best Imaging Tests for Rotator Cuff Tears
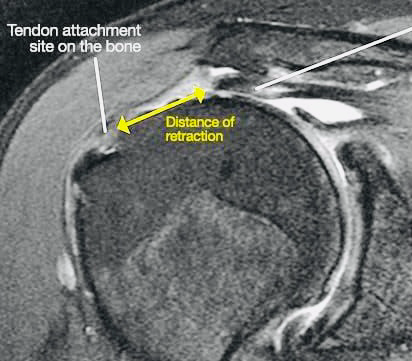
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
- Gold standard for diagnosing rotator cuff tears.
- Helps assess muscle quality, tear size, and degree of retraction.
- Detects biceps tendon pathology and subscapularis tears.
2. X-Rays
• Not commonly used but may show calcifications or humeral head migration in chronic cases.
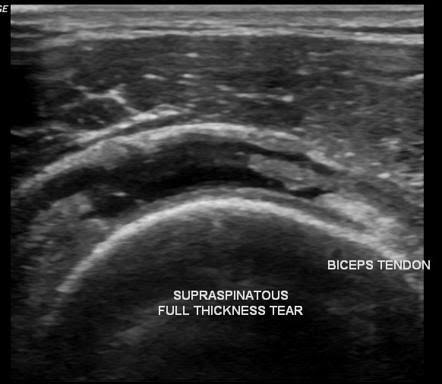
3. Ultrasound
• Affordable and dynamic, allowing real-time assessment.
• Highly user-dependent, requiring an expert radiologist.
start=”4″>
- Arthrogram (Less Common)
- Used when MRI is contraindicated.
- Dye leaks into the subacromial space, confirming a tear.
Best Treatment Options for Rotator Cuff Tears
Non-Surgical (First-Line Treatment)
- Physiotherapy – Strengthening of rotator cuff and scapular stabilizers.
- NSAIDs – Pain relief and inflammation control.
- Subacromial Corticosteroid Injections – Used for impingement-related pain (not for full-thickness tears).
Best Shoulder Surgeon & Physiotherapy Team in Gurgaon
For rotator cuff injuries, a combined approach with the best shoulder surgeon and expert physiotherapy team is crucial. At our center, we offer personalized rehabilitation programs to restore shoulder function.
Surgical Treatment (For Severe or Persistent Cases)
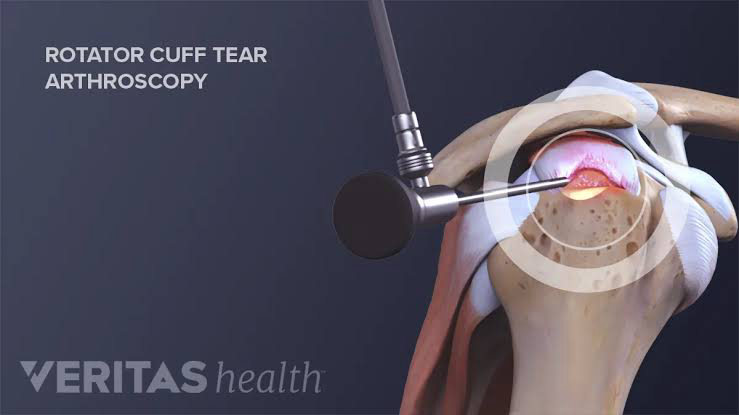
- Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair
- Minimally invasive procedure using a camera and small instruments.
- Indicated for bursal-sided tears >3 mm or articular-sided supraspinatus tears >7 mm.
- Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair
Best option for athletes and young active patients
- SpeedBridge™ Rotator Cuff Repair
- Advanced technique using medial ripstop sutures and SwiveLock® anchors for stronger repair.
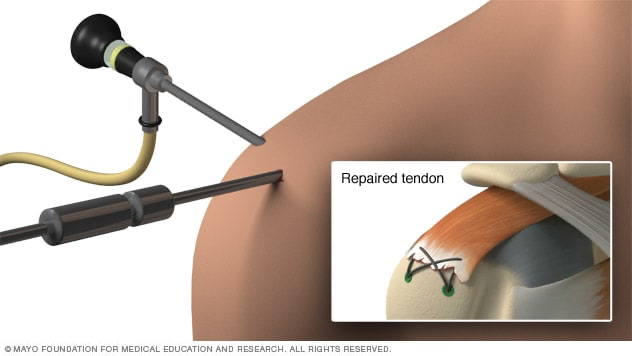
- Biological Healing & Recovery
- Healing takes 8-12 weeks as the tendon reattaches to the greater tuberosity of the humerus.
- Holes drilled into the greater tuberosity provide vascular supply for healing.
Why Choose Us for Shoulder Treatment in Gurgaon?
At AOSC we provide the best shoulder treatment in Gurgaon with a highly experienced team of shoulder surgeon and physiotherapist. Whether you need non-surgical management or advanced arthroscopic surgery, we ensure the best outcomes for your rotator cuff injury.
