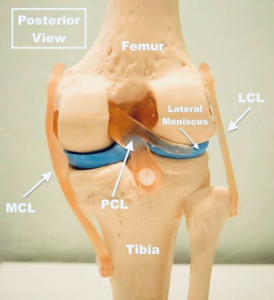
POSTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT
The Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL) plays a crucial role in stabilizing the knee by preventing the posterior displacement of the proximal tibia on the distal femur. Measuring approximately 36-39 mm in length and 11-13 mm in diameter, the PCL consists of two distinct bundles: the anterolateral bundle (ALB) and the posteromedial bundle (PMB). Along with treating PCL injuries, we specialize in advanced orthopedic procedures such as shoulder arthroscopy, providing comprehensive musculoskeletal care
- Symptoms include swelling, pain, and difficulty bearing weight.
- The most common complaint is pain, especially during long-distance walking or descending stairs.
- Pain is usually felt behind the patella and on the inner (medial) side of the knee.
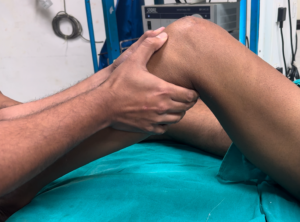
Posterior drawer test
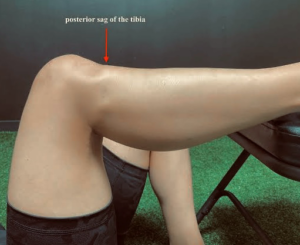
Posterior sag test of Godfrey:
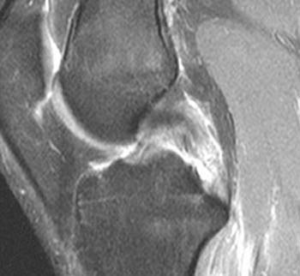
Investigations
MRI is the modality of choice to confirm clinical diagnosis of PCL rupture and evaluate for concomitant pathology.
Treatment Options
The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the injury and the patient’s condition. Nonoperative Management:- Isolated Grade I and II PCL injuries without instability can be treated without surgery.
- Grade II injuries with instability require surgical intervention.
- Treatment includes protected weight-bearing and rehabilitation, focusing on quadriceps strengthening to improve knee stability.
- PCL repair or reconstruction is needed for Grade II injuries with instability, Grade III injuries, and multi-ligament injuries.
- Bony avulsion fractures may require surgical repair.
- Open surgery is now rare due to advancements in arthroscopic techniques.
- This technique is suitable for all age groups but only for fresh injuries.
- In delayed cases, other surgical options are preferred.
- The procedure is done arthroscopically, where the torn ligament is reattached to its footprint using suture anchors.
- We use FiberTape internal bracing for added stability, allowing faster rehabilitation and an early return to sports, helping patients regain confidence quickly.
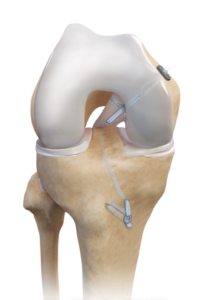
PCL Reconstruction
- For combined injuries, repair or reconstruction should be done within 10–14 days to prevent fixed posterior tibial translation.
- Delayed treatment can lead to capsular scarring and collateral ligament atrophy, making recovery more challenging.
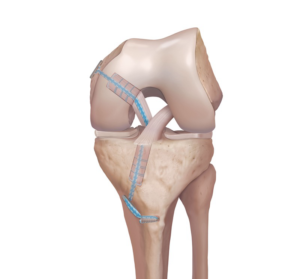
We use one hamstring graft for PCL reconstruction. Native PCL stump is preserved to save proprioception nerve endings. The hamstring graft with FiberTape is fixed to the bone using Tight Rope RTJ, Tight Rope loop & Conical Button made in USA (ARTHREX). We don’t use bioscrew because of weaker stability compared to Tight Rope loop & Conical Button.
Dr. Nitin rawal, Sports injury and joint replacement specialist prefers only All Inside PCL Reconstruction with Fiber Tape Internal Bracing which prevents postoperative ligament loosening and failure of graft, it also promotes painless and faster recovery. Best PCL treatment by dr Nitin rawal and his team in Gurgaon.
